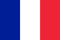
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate that affects men over the age of 20.
According to statistics, 1 in 4 men has experienced this disease in one form or another. In recent years there has been an ongoing tendency to "rejuvenate" the process. This is due to sexual liberation, an increase in sexually transmitted infections, tendencies towards self-diagnosis and treatment on the Internet and the resistance of infectious agents to the effects of antibiotic therapy.
This is especially true because the first signs of prostatitis in men, as a rule, are erased, which does not allow timely consultation with a doctor and, in some cases, leads to the development of advanced prostatitis.
Signs of prostatitis in men
Features of the structure, blood supply, and location of the prostate will affect the type of symptoms that lead to its inflammation. These include:
- Pain symptom.
- Symptom of urinary tract disease (dysuria).
- Erectile dysfunction symptom.
Pain symptom
Sensations of pain of varying intensity disturb the man in the lower abdomen, in the perineum, in the genitals and in the lumbosacral spine. This pain point is due to the presence of nerve connections and the involvement of the seminal vesicles (vesicles) in the inflammatory process.
The intensity of the pain can vary, from an unexplained feeling of discomfort to severe pain that affects a man's state of mind and causes insomnia. Pain sensations depend on sexual behavior and arise from the lack of regular ejaculation or, conversely, from ejaculation associated with the spread of the inflammatory process on the posterior urethra.
Note that pain in the lumbosacral region may not be associated with the prostate in any way, but could be the result of, for example, osteochondrosis of the spine. The result of a conversation with the patient and the data of the urological examination will help establish the cause of such pain.
The very first sign of prostatitis in a man is a sensation of pain in the testicles (scrotum area) that spreads along the epididymis (right and left groin area). Pain emanating from an inflamed prostate can occur on the inner thighs and back. This dictates the need to consult a neurologist to rule out a neurological pathology, since such spread is not typical, especially with prostate pain.
In some cases, the irradiation of painful sensations is asymmetrical, which makes it possible to suspect an inflammatory process in the prostate, which is localized in one of its lobes. At the place of manifestation, the pain syndrome is divided into genitals (in the genital area), characteristic of congestive chronic prostatitis), extragenital (above the genital organs), characteristic of advanced advanced prostatitis) and mixed (chronic prostatitis).
Symptoms of dysuria or urinary tract disease with prostatitis
Urination disorders are manifested as false wishes, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder with frequent urination, which is associated with inflammation in the bladder neck and urethra. The long-standing signs of dysuria in prostatitis indicate the chronicity of the process.
Erectile dysfunction with prostatitis

Erectile dysfunction in prostatitis is represented by early ejaculation, blurred sensations during orgasm, decreased libido, and weakening of the erection. Sometimes a man's prostatitis can be suspected by the lack of morning erections.
A decrease in effectiveness as the first sign of prostatitis in a man is caused by a decrease in testosterone synthesis (male sex hormone).
The manifestations of inflammation in the prostate are not limited to the above three symptoms. Often the first sign of prostatitis in a man is the discharge of prostate secretion from the urethra during bowel movements (prostatorrhea), which indicates a decrease in the muscle tone of the ejaculatory ducts.
In addition, one can only focus on the psychological signs of prostatitis in a man: the astheno-neurotic syndrome develops from the nervous system (depression, fatigue, lack of desire to do something, physical weakness).
The first signs of acute prostatitis
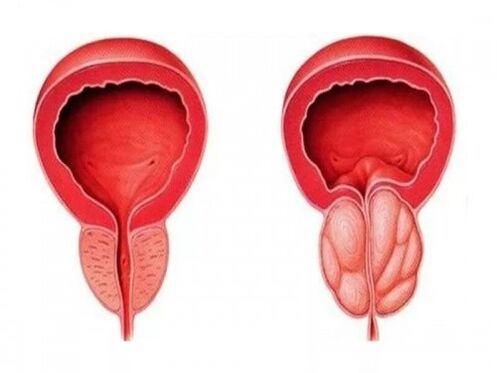
All of the above symptoms are typical of chronic inflammation in the prostate, with acute prostatitis in a man the picture is slightly different.
The disease begins with acute severe pain in the perineum, symptoms of a urinary disorder are more clearly visible. There is an increase in temperature to 38-39 ° C, chills, weakness, sweating, pain in muscles and bones. When defecating, pain in the anus worries. There is no such thing as a sex life.
If you do not pass the examination in a timely manner and do not start treatment, the acute process will be complicated by purulent prostatitis, up to and including an abscess, which will lead to emergency surgery.
If there are no other reasons (states of immunodeficiency, severe concomitant disease, etc. ) - purulent prostatitis in a man - an advanced inflammatory process due to early access to a doctor!
Causes of Signs of Inflammation of the Prostate
The factors influencing inflammation in the prostate have traditionally been divided into three groups.
Unresponsive factors include:
- Body type.
- Sexual constitution.
- Age factor.
- The presence of diseases.
- Environment (climate factor).
Partly controllable factors:
- Sexual habits.
- Job.
- Background diseases of the male genital area.
- Attitude to illness.
And finally controllable factors:
- Promiscuous sex life.
- Alcoholism.
- Failure to comply with treatment recommendations.
- Power mode error.
Who is at risk
Prostatitis threatens men who:
- Stick to a sedentary lifestyle.
- Suffer from chronic constipation.
- Have a history of sex infections.
- Have more than one sexual partner.
- Suffering from alcoholism, drug addiction.
- You work in cold conditions.
What to do if there are signs of prostatitis
Laboratory diagnostics for prostatitis

- In the KLA an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. With OAM - leukocyturia, proteinuria, bacteriuria.
- Blood for HIV infection.
- A smear from the urethra on the flora. As a rule, leukocytes in the smear are complete. If a sex pathogen (Neisser's gonococci, Trichomonas) is not identified, a PCR diagnosis must be carried out.
- Secretion of the prostate. Sowing the secretion of the prostate on the causative agent and determining the sensitivity to the antibiotic.
- PCR diagnostics for sexually transmitted infections. The most reliable and fastest way to verify the pathogen.
- Blood for PSA Blood for PSA (prostate-specific antigen) should not be drawn during an acute inflammatory process in the prostate; the result is unreliable. It is better to do this analysis 1 month after the end of therapy. There is no need to test blood PSA levels for young people under the age of 30. This test is important for a man over 40 because acute prostatitis can be secondary in some cases and a malignant tumor in the prostate is masked behind its clinical manifestations.
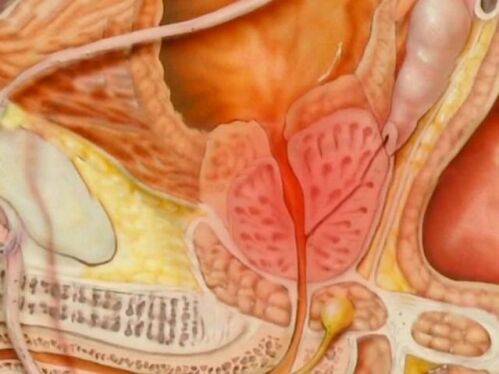
Instrumental diagnostic methods
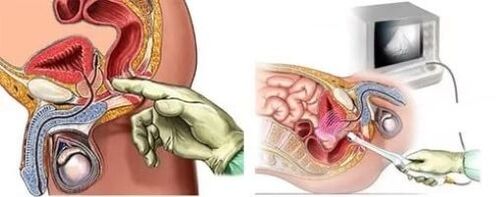
Usually, an ultrasound scan of the prostate transrectally (through the rectum) or transabdominally (through the abdomen) is sufficient.
Signs of prostatitis on ultrasound
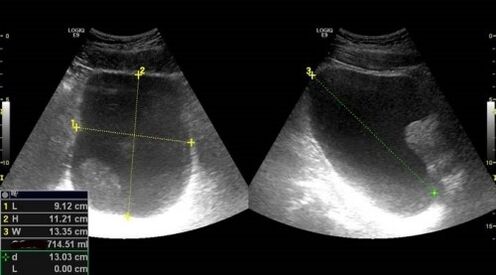
An increase in the volume of the gland, a change in texture, edema; with purulent prostatitis - areas with necrosis, deformation of the contours, increase in regional lymph nodes.
What to look out for
First of all, in order to get rid of the symptoms of prostatitis forever, you need to follow a certain diet.
The exacerbation of prostatitis in a man depends on irritating substances that are ingested with food: hot spices, vinegar, cucumber, alcohol.
Of particular note is alcohol, the minimal use of which can negate the effects of complex long-term therapy.
Some patients feel they should drink less often or switch to lighter alcoholic beverages. This is their main flaw.
Diluted vinegar, kvass, citrus fruits, sauerkraut, tomatoes and cucumbers do not have a harmful effect on prostatitis.
Eating high fiber foods relieves a man from constipation - one of the main reasons for developing constipation in the pelvis.
Herbal medicine helps well in prevention. Taking herbal diuretics: cranberry leaf, dill seeds, urological collection helps improve urination during inflammation.
Sports, especially sports that improve blood flow to the pelvic organs, help keep the prostate in good shape.
The development of inflammation in the prostate leads to hypothermia. In winter it is worthwhile to dress warmer, and in summer you shouldn't be in wet swimming trunks for a long time after swimming.
Using condoms during sexual contact with an unknown partner will protect you from sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV infection.
Prolonged fatigue has a negative impact on a man's immune system as well as stressful situations that can exacerbate dormant prostate infection. Regular preventive examinations by a urologist help maintain men's health.